In today’s technologically advanced world, glass plays a pivotal role in various industries, from electronics to architecture, and from retail displays to scientific research. Among the many types of glass available, anti-reflective glass has emerged as a transformative material, particularly in applications where clarity, visibility, and precision are paramount. But what exactly makes anti-reflective glass so essential, and why is it rapidly becoming a game changer in both optical and architectural solutions?
Anti-reflective glass, as the name suggests, is a type of glass treated with a special coating to reduce the amount of light reflected off its surface. This coating is typically composed of one or more layers of materials with different refractive indices, designed to minimize reflection by allowing more light to pass through the glass. The result is a significant improvement in optical clarity, making the glass virtually transparent and enhancing its overall performance in various applications.
Content
How Does Anti-Reflective Glass Work?
The fundamental principle behind anti-reflective glass is the interference effect. When light strikes a surface, part of it is reflected while the rest passes through. The reflective coating on anti-reflective glass is engineered to interact with the light waves in such a way that the reflected light waves cancel each other out. This interference reduction dramatically decreases the reflection and glare, improving the light transmission through the glass.
The coating typically consists of a thin layer of oxide material, such as silicon dioxide (SiO2) or magnesium fluoride (MgF2), applied through processes like vacuum deposition or sol-gel coating. These layers are engineered to match the wavelength of light they are most likely to interact with, making the glass more transparent and reducing the loss of light that usually occurs when light reflects off traditional glass surfaces.
What Are the Key Benefits of Anti-Reflective Glass?
-
Enhanced Visibility and Clarity
The most obvious benefit of anti-reflective glass is its ability to improve visibility by reducing glare and reflection. In everyday scenarios, such as looking through windows or using digital devices like smartphones and computers, the reflections can significantly hinder the viewing experience. By allowing more light to pass through and minimizing visual distortion, anti-reflective glass ensures crisper images and clearer views, enhancing user experience across a range of applications. -
Improved Aesthetic Appeal
From a design perspective, anti-reflective glass offers a sleek, modern appearance. In architectural applications, such as facades, skylights, and glass walls, the reduced reflection creates a more seamless visual integration with the surroundings. Buildings that use anti-reflective glass appear less intrusive and provide cleaner lines, contributing to an overall more aesthetically pleasing and contemporary structure. -
Increased Light Transmission
In applications like solar panels or optical instruments, maximizing the amount of light passing through the glass is crucial. Anti-reflective glass is engineered to allow up to 99% of light transmission, significantly increasing the efficiency of solar cells or enhancing the performance of optical equipment, such as microscopes, telescopes, and cameras. This higher transmission means better performance with less light loss. -
Reduced Eye Strain
In electronic displays and screens, especially for smartphones, televisions, and computer monitors, the reduction of glare can significantly reduce eye strain caused by prolonged exposure to bright, reflective surfaces. Anti-reflective coatings on these devices contribute to a more comfortable viewing experience, minimizing the need for users to adjust their surroundings or screen brightness to compensate for glare. -
Protection and Durability
Anti-reflective glass often comes with added scratch resistance and protective coatings, making it more durable and longer-lasting than standard glass. These additional coatings also help in maintaining the glass’s transparency over time, ensuring that its performance does not degrade due to everyday wear and tear.

What Are the Common Applications of Anti-Reflective Glass?
-
Architectural Use
In modern architecture, especially for storefronts, facades, and curtain walls, the demand for glass that offers both transparency and minimal reflection is ever-growing. Anti-reflective glass is increasingly being used in high-end commercial buildings, luxury homes, and retail displays. Its ability to enhance natural light while reducing visual clutter from reflections makes it a popular choice for building projects that require both form and function. -
Optical and Display Devices
Anti-reflective glass is a crucial component in eyewear (such as glasses and sunglasses), optical lenses, and camera lenses. For devices like smartphones, tablets, and computers, it is commonly used for touchscreens and displays, where reduced reflection improves the viewing experience in various lighting conditions. The film or coating applied to the glass improves the visibility of images, and reduces eye fatigue in users. -
Solar Energy Solutions
One of the most significant applications of anti-reflective glass is in solar panel production. Solar cells coated with anti-reflective glass capture more sunlight, which leads to higher energy efficiency. The reduction of light reflection ensures that a maximum amount of solar energy is absorbed, improving the overall performance of the solar power system. -
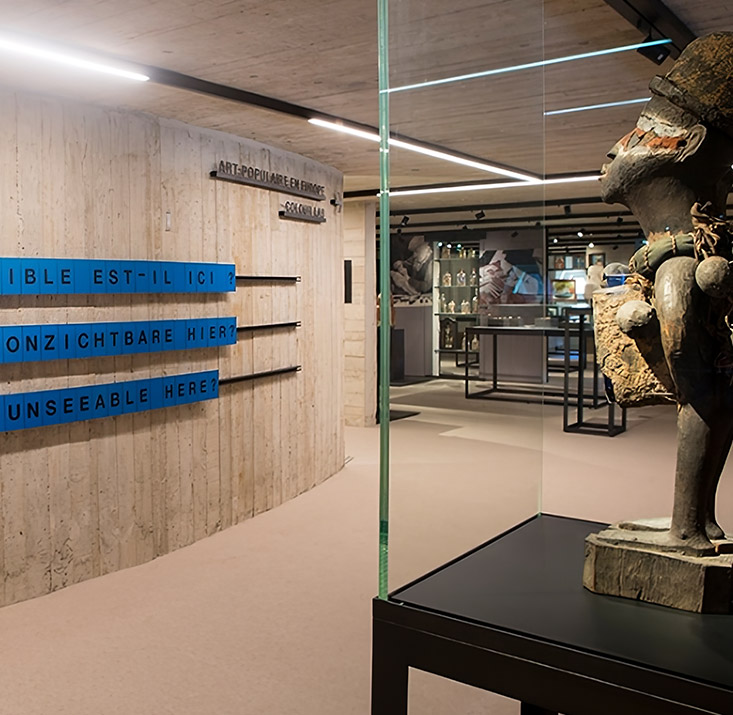
Museum and Display Cases
In museums and galleries, anti-reflective glass is often used for framing artwork or in display cases where the goal is to allow viewers to appreciate the artwork without distractions from glass glare. This type of glass provides an almost invisible barrier between the observer and the object, ensuring a more immersive experience.
What Does the Future Hold for Anti-Reflective Glass?
As technology advances, so does the development of anti-reflective coatings. The next generation of anti-reflective glass is expected to incorporate more advanced nanotechnology, enhancing its properties even further. New coatings could provide self-cleaning capabilities, greater durability, and increased environmental resistance. Additionally, as the demand for sustainable and energy-efficient materials continues to rise, anti-reflective glass will likely play an increasingly important role in green building practices, particularly in applications that require energy-efficient windows or solar energy systems.