Preserving the past while presenting it to the public is a central mission for any museum. Whether the institution specializes in ancient artifacts, fine art, rare manuscripts, or natural history specimens, one constant remains: the need to protect priceless objects from environmental and physical harm. While traditional glass has been used for decades in museum display cases, modern materials science has introduced a more advanced solution—anti-deformation glass. This innovative glazing option is increasingly becoming a necessity for institutions that value both protection and presentation quality.
This article explores why museums should seriously consider upgrading to anti-deformation glass, detailing its properties, advantages, and applications within exhibit environments.
Content
- 1 What Is Anti-Deformation Glass?
- 2 The Importance of Structural Stability in Museum Displays
- 3 Key Benefits of Anti-Deformation Glass in Museums
- 4 Where Anti-Deformation Glass Is Used in Museums
- 5 Considerations When Choosing Anti-Deformation Glass
- 6 A Practical Example: Replacing Traditional Panels in Historical Collections
- 7 Cost vs. Long-Term Value
- 8 Conclusion: A Smart Investment for Preservation and Presentation
What Is Anti-Deformation Glass?
Anti-deformation glass is a high-performance type of glass specifically engineered to maintain structural flatness and optical clarity even under long-term stress. It resists bending, warping, and sagging, especially in large display cases where conventional glass may lose integrity over time. It may also be treated with coatings or laminated with additional layers for UV protection, anti-reflection, or added strength.
Unlike standard float glass, which can gradually distort due to internal stress or changes in temperature and humidity, anti-deformation glass holds its shape and surface uniformity over the long term—ensuring that museum displays are protected and remain visually accurate.
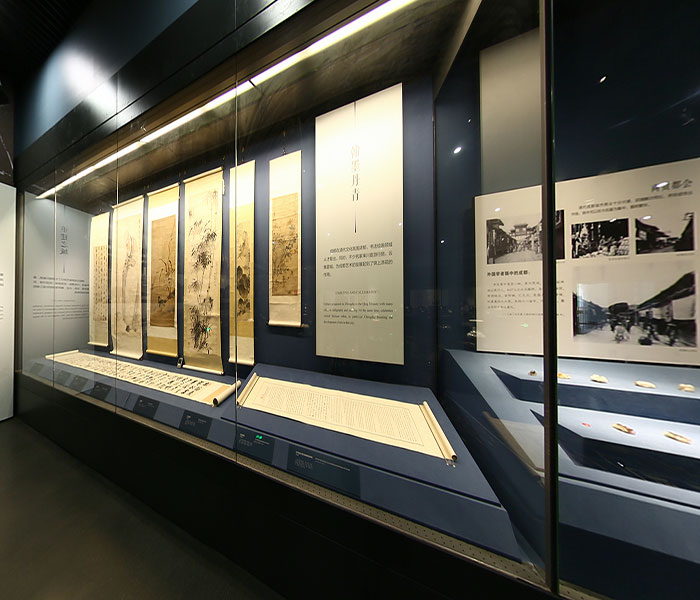

The Importance of Structural Stability in Museum Displays
When glass warps or bends, it affects more than just aesthetics. Deformation can compromise the protective enclosure in several ways:
Reduced Sealing Efficiency: Warped glass can cause gaps in the display case seals, allowing dust, pollutants, and insects to enter.
Optical Distortion: Deformed glass creates visual distortion, which affects the visitor experience and diminishes the intended impact of the display.
Increased Risk of Breakage: Once glass loses its original shape, stress points may develop that make the panel more vulnerable to cracking or shattering.
Security Vulnerability: In some cases, deformed glass may not align properly with locking mechanisms, reducing the effectiveness of security systems.
For museums that prioritize long-term preservation and display accuracy, these are not small concerns. Anti-deformation glass directly addresses each of these risks.
Key Benefits of Anti-Deformation Glass in Museums
1. Long-Term Display Integrity
Artifacts and artwork are often displayed for years or even decades. Anti-deformation glass ensures that the display cases remain stable over time, eliminating the gradual shifts and warps seen in conventional materials. This is particularly important for tall or wide vitrines where gravity and pressure differentials exert more force on the glass panels.
2. Enhanced Visitor Experience
Museum visitors expect to see exhibits clearly and accurately. Warped or bowed glass can reflect light unevenly or create “funhouse mirror” effects that distract from the artifact. Anti-deformation glass retains flatness and optical clarity, offering viewers an undistorted and immersive visual experience.
3. Improved Environmental Protection
Properly sealed and stable cases are essential for preserving objects sensitive to light, humidity, and pollutants. Anti-deformation glass supports case integrity by reducing movement and gaps that could let in harmful environmental elements. This also reduces the workload on climate control systems within the case.
4. Compatibility with Specialized Coatings
Many anti-deformation glass types can be enhanced with anti-reflective coatings, UV-blocking layers, or laminates that further increase safety and visibility. These features help protect light-sensitive documents or paintings while reducing glare and reflections that interfere with viewing.
5. Security and Theft Prevention
Flat, strong, and well-fitted glass panels are harder to pry open or damage. Anti-deformation glass supports robust locking systems and helps maintain structural integrity under potential physical tampering or external force.
Where Anti-Deformation Glass Is Used in Museums
Anti-deformation glass is suitable for a wide variety of museum installations:
Freestanding display vitrines
Wall-mounted cases
Archival document frames
Interactive display barriers
Protective glazing over paintings and artifacts
Glass-top display tables
Large-format cases that span over 1 meter in height or width benefit the most from the glass’s resistance to bowing. Additionally, traveling exhibits and modular installations—frequently subject to handling and environmental changes—are safer with anti-deformation panels.
Considerations When Choosing Anti-Deformation Glass
When selecting anti-deformation glass for a museum project, several factors should be evaluated:
1. Glass Thickness and Weight
While thicker glass offers more rigidity, it also adds weight, which can affect structural supports and portability. Anti-deformation glass balances stiffness and manageability, often available in multiple thicknesses optimized for museum display needs.
2. Clarity and Color Fidelity
Ensure that the selected glass type has minimal color cast (green or blue tints) that could affect the perception of displayed objects. Low-iron variants offer superior clarity for color-accurate presentation.
3. Custom Fabrication and Fitting
Anti-deformation glass should be precision-cut and finished to exact specifications, particularly for airtight display cases. Work with experienced museum glass fabricators who understand the importance of both aesthetics and protective function.
4. Integration with Lighting Systems
Because lighting and reflections play a critical role in exhibit design, it’s worth coordinating the use of anti-deformation glass with planned lighting angles, especially if anti-glare or anti-reflection coatings are used.
A Practical Example: Replacing Traditional Panels in Historical Collections
Let’s say a history museum is upgrading its colonial artifact collection, housed in a large custom-built display wall. The original float glass panels, after 15 years, are showing signs of curvature and edge distortion, creating light pockets and small air leaks.
By replacing those with anti-deformation glass panels, the museum can restore the visual crispness of the exhibit while improving humidity control and prolonging the life of sensitive artifacts like textiles and paper items. This also reduces the maintenance load, as fewer adjustments and resealing efforts are required over time.
Cost vs. Long-Term Value
While anti-deformation glass may carry a higher upfront cost compared to standard options, its long-term advantages—such as reduced maintenance, fewer replacements, better object preservation, and improved visitor satisfaction—can offer a strong return on investment. Many museums have found that the durability and low maintenance requirements of anti-deformation glass actually lower lifetime costs.
Conclusion: A Smart Investment for Preservation and Presentation
Museums today are more than just repositories of the past—they are centers of education, culture, and public engagement. Display quality and object safety are fundamental to that mission. Anti-deformation glass offers a modern, high-performance solution that supports both conservation and curation goals.
For institutions seeking to elevate their exhibit environments and preserve collections under optimal conditions, upgrading to anti-deformation glass isn’t just a premium option—it’s a forward-thinking investment in the future of heritage preservation.