Anti-reflective glass has become a key material in industries where visibility, precision, and aesthetics are critical. By significantly reducing unwanted reflections on the surface of glass, it ensures higher light transmission and a clearer view. From architectural glazing to high-tech electronics, anti-reflective glass offers a balance of function and design that meets the growing needs of modern construction and technology.
Content
1. The Principle Behind Anti-Reflective Glass
When light strikes ordinary glass, part of it is reflected while the rest passes through. This reflection often causes glare, reduces contrast, and lowers visibility. Anti-reflective glass solves this problem by applying a thin coating that alters the refractive index of the surface. Through this technology, reflected light is minimized, and light transmission can reach up to 98%, creating a crystal-clear viewing experience.
2. Distinctive Features
- Superior transparency – Offers maximum light penetration for natural brightness.
- Glare reduction – Minimizes eye strain, especially in environments with strong lighting.
- True color rendering – Displays objects and images with enhanced clarity.
- Scratch and abrasion resistance – Special coatings extend the service life of the glass.
- Adaptability – Can be used as laminated, insulated, or tempered glass to meet safety requirements.
3. Advantages of Using Anti-Reflective Glass
- Improved visibility in public spaces – Perfect for museums, galleries, and retail stores.
- Energy-saving benefits – Increased natural daylight reduces reliance on artificial lighting.
- Modern aesthetic – Provides a sleek, transparent appearance that enhances architectural design.
- Reliable performance in outdoor use – Resistant to UV exposure and environmental conditions.
- Versatile applications – Supports industries from solar energy to consumer electronics.
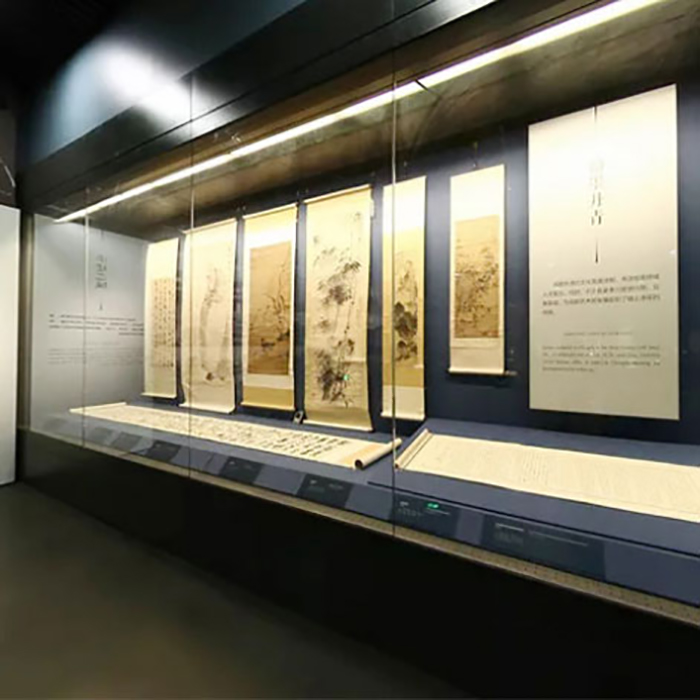

4. Key Application Areas
-
Architecture and Interiors
Anti-reflective glass is used in windows, skylights, and glass facades to maximize daylight entry while eliminating glare. It improves comfort in offices, homes, and commercial buildings. -
Exhibitions and Retail
In display cases, jewelry counters, and museum showcases, anti-reflective glass ensures visitors see the exhibits without distractions from reflections. -
Technology and Electronics
Widely used in monitors, tablets, smartphones, and control panels, it enhances screen readability even under bright light. -
Solar Energy Systems
AR glass boosts solar panel efficiency by allowing more sunlight to reach photovoltaic cells. -
Automotive and Transportation
Anti-reflective coatings on instrument panels, dashboards, and navigation displays improve visibility for drivers.
5. Types of Anti-Reflective Glass
- Single-sided coated glass – Reduces reflection on one surface, suitable for standard uses.
- Double-sided coated glass – Minimizes glare from both sides, ideal for high-performance applications.
- Customized wavelength AR glass – Designed for specialized optical instruments and solar modules.
6. Care and Maintenance
Anti-reflective glass is durable, but proper cleaning ensures long-term performance:
- Use non-abrasive cleaners and soft microfiber cloths.
- Avoid harsh chemicals that may damage the coating.
- Regular maintenance preserves both transparency and coating integrity.
7. Industry Outlook and Future Developments
The global demand for anti-reflective glass is steadily increasing, driven by sustainable construction and advanced electronics. Emerging trends include:
- Multifunctional coatings – Combining anti-reflection with anti-fog, self-cleaning, and UV protection.
- Integration in smart buildings – Paired with energy-efficient low-E coatings for intelligent glazing.
- Applications in wearable technology – Used in smart glasses, AR/VR devices, and next-generation optics.
8. Conclusion
The anti-reflective glass plays a vital role in improving visual comfort, energy efficiency, and design quality across multiple industries. With its ability to reduce glare, enhance clarity, and adapt to different environments, it has become a preferred choice for architects, manufacturers, and technology developers. As innovations in coating technology continue, anti-reflective glass will remain central to both functional and aesthetic advancements in modern applications.