In the field of modern building design and decoration, innovations in material science continue to provide designers and architects with new tools to shape space, enhance functionality, and create aesthetic appeal. Low-reflective glass, a material with unique optical properties, has emerged in recent years as an important material for creating high-quality visual environments. The ability of this glass to significantly reduce the reflectivity of light, minimizing glare while providing a clear transmission of vision, has led to innovative applications in some areas.
Firstly, the use of low-reflective glass in the architectural sector is particularly noteworthy. Whereas ordinary glass with high reflectivity often leads to discomfort and energy wastage due to daylight reflection, low-reflective glass effectively avoids this problem. In large-scale curtain wall projects, the use of low-reflective glass can significantly reduce light pollution to the surrounding environment, while allowing natural light to enter the room more gently, which not only improves the comfort of the interior of the building but also saves the energy consumption of lighting. In addition, it can also provide a certain degree of privacy protection for the interior while maintaining good light transmission.
Secondly, low-reflection glass is increasingly used in optical equipment. For example, in telescopes, camera lenses various types of displays, and other precision optical equipment, low-reflection glass can reduce the loss of light caused by internal reflection to improve the quality of imaging. This is crucial for specialized areas where images need to be observed and recorded accurately.

Furthermore, low-reflective glass also plays an important role in vehicle design. Low-reflective glass for car windows not only reduces the dazzling effect of sunlight and increases driving safety, but also gives car designers more freedom to create a streamlined appearance.
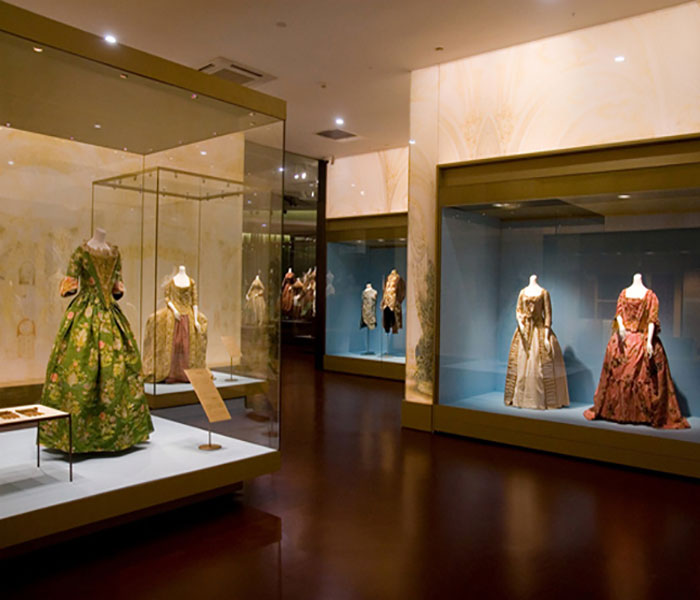
In addition to these areas, the unique properties of low-reflective glass have led to a wide range of applications in art display, lighting design, and the eyewear industry. In art galleries and museums, low-reflective glass effectively reduces reflections on the surfaces of exhibits, allowing viewers to appreciate the artwork more clearly. In lighting design, it is used to make lampshades that produce a soft and even distribution of light, creating a warm and comfortable atmosphere. For the eyewear industry, especially high-end sunglasses and optical lenses, the application of low-reflective coating technology not only improves the anti-glare properties of the lenses but also increases the aesthetics and practicality of the products.
However, despite the many benefits offered by low-reflective glass, there are still some challenges to be faced in practical applications. For example, the durability and maintenance issues of low-reflection coatings, as well as the stability of their performance in different environments, require further research and technological breakthroughs. In addition, the cost factor is also an important constraint to its wide application. Therefore, researchers and engineers are working hard to develop more cost-effective production methods to promote the popularity and development of low-reflective glass technology.
In conclusion, low-reflective glass is gradually transforming our living environment with its unique advantages. From skyscrapers to delicate watch faces, from optical instruments to everyday eyewear, the application of low-reflection glass is like a symphony of light and shadow, bringing comfort and clarity to our visual experience. With the development of technology, we have reason to believe that low-reflective glass will show its brilliant light in more fields.