In contemporary society, as technology continues to advance and people's aesthetic needs increase, low-reflective glass has gradually become an important material for improving our living space. This special glass is playing an increasingly important role in several areas with its properties of reducing light reflection and increasing light transmission. In this article, we look at the properties of low-reflective glass, its applications, and how it affects our daily lives.
Low-reflective glass, also known as low-emissivity glass or anti-reflective glass, has been treated with a special process that results in a surface with extremely low light reflectivity. Generally speaking, ordinary glass reflects about 8% of visible light, while low-reflection glass can reduce this percentage to less than 2%, thus greatly reducing light loss and glare caused by reflection.
In the eyewear industry, low-reflective glass is particularly widely used. For eyeglass wearers, reflections not only affect visual clarity but can also cause eye fatigue for those who work long hours in front of a computer screen. Low-reflective glass lenses can effectively reduce this discomfort and provide a more comfortable visual experience. In addition, this glass is also used in the production of precision optical instruments such as telescopes and microscopes due to its desirable optical properties.
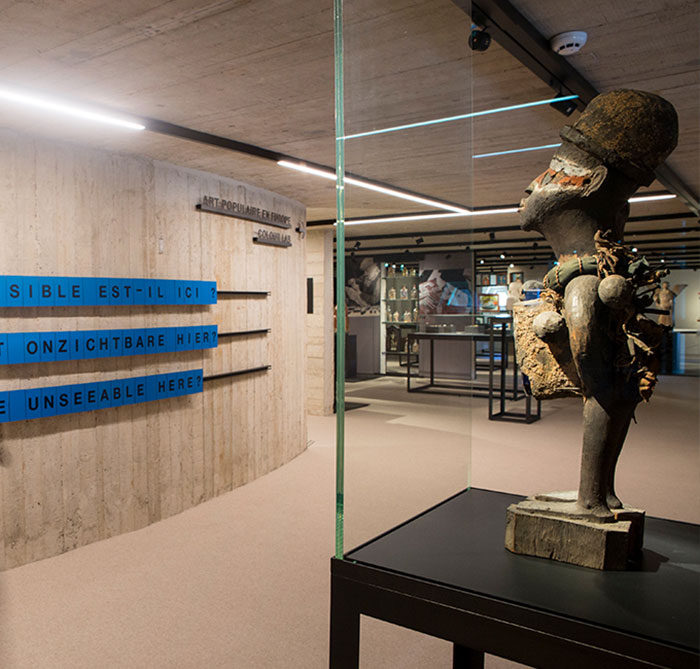

In the field of architecture, the application of low-reflective glass should not be underestimated. Modern architectural design emphasizes the need for both natural lighting and energy saving, and low-reflection glass meets this need. It can provide a better light transmission effect, make the indoor light more uniform and soft, and at the same time reduce the interference of the external line of sight, for indoor personnel to create a more private space. The use of low-reflective glass curtain walls on the facades of high-rise buildings not only reduces urban light pollution but also reduces energy consumption caused by the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor areas.
In addition to these applications, low-reflective glass also plays an important role in photography, stage lighting, art exhibitions, and other fields. Photographers use lenses made of low-reflective glass to capture purer light, while theatres and exhibition halls use it as display windows to give audiences a better viewing experience.
However, the use of low-reflective glass is not without its challenges. Cost is one of the main constraints to its widespread use. The production process for low-reflective glass is relatively complex, resulting in a higher cost than ordinary glass. However, this issue is expected to be alleviated as the technology continues to mature and large-scale production advances.
Environmental friendliness is also an issue to be considered for low-reflective glass. While it helps to reduce energy consumption and minimize light pollution, its production and recycling processes should also comply with the requirements of sustainable development. Manufacturers therefore need to develop more environmentally friendly production techniques and ensure the recyclability of their products.
In conclusion, low-reflective glass, as an advanced material technology, is gradually permeating every aspect of our lives. From improving the personal visual experience to optimizing the urban built environment to enhancing the quality of art appreciation, low reflective glass brings us brighter, clearer, and more efficient living spaces. As technology advances and applications expand, we can expect this material to play an even greater role in the future, further improving the quality of human life.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)